Emergency contraception refers to contraception methods that are used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected sexual intercourse. It is also called Plan B, the Morning after Pill or Post Coital Contraception. You should take it, if you did unprotected sex in your fertile period and do not want pregnancy. They are more effective at 99% if taken within first 12 hours after intercourse but can still be effective in 5 days. Available option include Oral pills such as levonorgestrel, ulipristal and combined pills and intrauterine device (IUD) which is inserted in uterus.
Levonorgestrel alone is less effective than ulipristal, but it is available over-the- counter. Levonorgestrel is more effective than the combination of estradiol plus levonorgestrel (Yuzpe regimen) and has a lower frequency of side effects. Apart from pills, IUD is the most effective among emergency contraception methods.
In this article, We will explore more on available methods, dosage, and mode of action, their effectiveness and side effects. We will go along with eligibility criteria for a woman to use emergency contraception and recommendations.
Available methods
Emergency contraception methods are in different forms. There is emergency contraception pills such as Levonorgestrel, Yuzpe regimen, Ulipristal and intrauterine device.
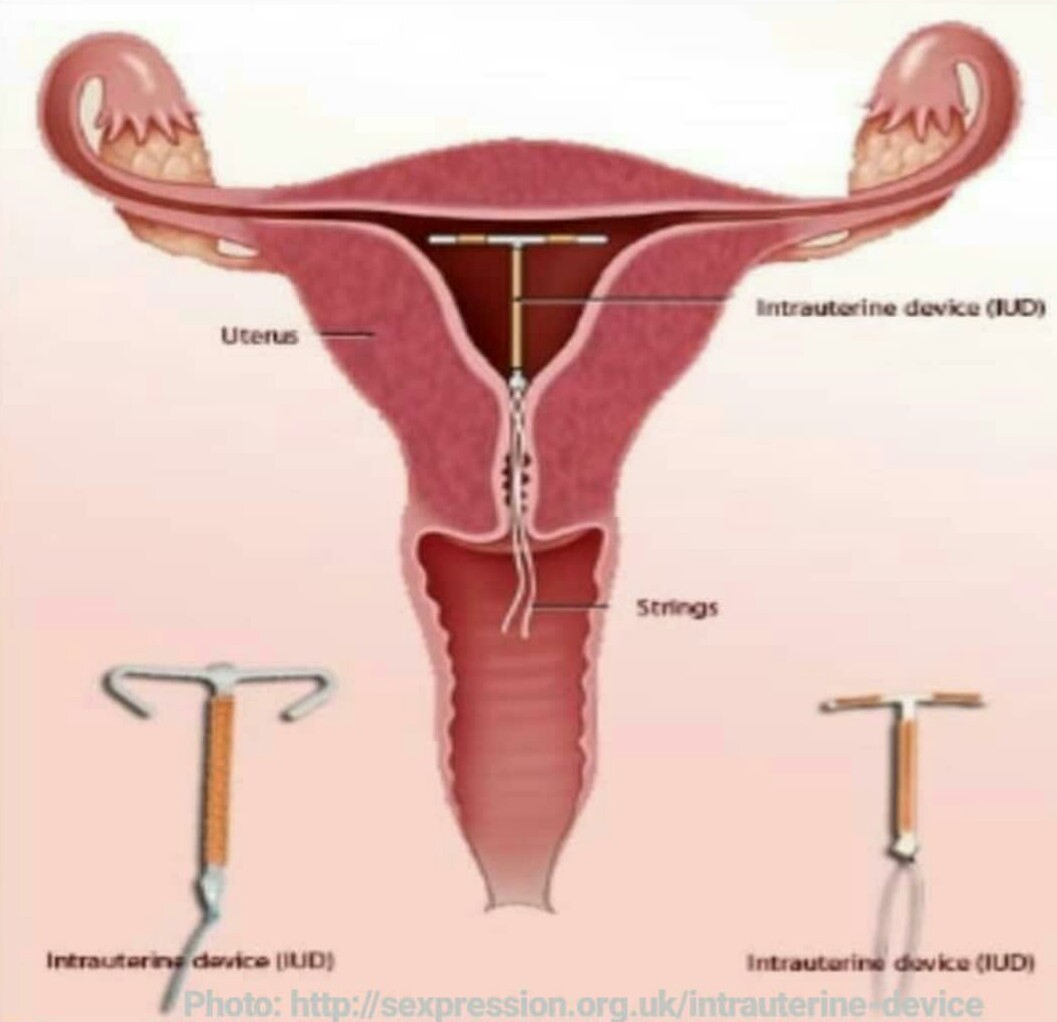
A copper-bearing IUD (intrauterine device) is the most effective form of emergency contraception available. A nurse, doctor or any skilled health care provider insert IUD into your uterus in sterile condition. Once inserted, women can continue to use the IUD as an ongoing method of contraception, or may choose to change to another regular contraceptive method. It is available to many health facilities in Rwanda but require skilled health care provider to insert.
Levonorgestrel is a hormonal medication, which is used in a number of birth control methods. It becomes less effective if it is taken longer after sex and only works before pregnancy has occurred. Levonorgestrel is widely available and does not require a prescription.
Yuzpe regimen pills (Estradiol plus levonorgestrel) is less effective and associated with more side effects than levonorgestrel alone. The Yuzpe regimen is rarely recommended. Despite these disadvantages, some women prefer estrogen- progestin contraceptive pills.
Ulipristal is a selective progesterone medication. It can delay ovulation by as much as five days. It works by inhibiting ovulation in the advanced follicular phase, a time when levonorgestrel emergency contraception is no longer effective. It can be used for emergency contraception up to 120 hours after intercourse. It is available and more effective than levonorgestrel but requires prescription.
Mechanism of action
Emergency contraceptive pills prevent pregnancy by preventing or delaying ovulation and do not induce an abortion. The copper-bearing IUD prevents fertilization by causing a chemical change in sperm and egg before they meet. They can also prevent pregnancy by interrupting implantation (after fertilization has occurred). Emergency contraception cannot interrupt an established pregnancy or harm a developing embryo. If you think, you are already pregnant do not use them.
EC Pills are temporal contraception methods. They are not intended to be used as a regular form of contraception. However, you can use emergency contraception several times. Doctor or nurse insert IUD (a T-shaped plastic and copper device) into your uterus. It releases copper to stop the egg implanting in your womb or being fertilized. The IUD can be inserted up to 5 days after unprotected sex. The more importantly for IUD, you can leave it for regular contraception. The unfortunate news is both methods are ineffective once implantation has occurred.
Effectiveness
IUD (Intrauterine device) can prevent unwanted pregnancy when taken within 120 hours after unprotected intercourse. If inserted shortly after sex, it is effective up to 99%. Ulipristal has a pregnancy rate of 1.2%, it is effective as Levonorgestrel within 48 hours and has shown great effectiveness to Lovenorgestrel after 48 hours up to 120 hours. Lovenorgestrel is effective at 95% when taken within 24hour and 89% after 72hour but can still up to 120 hours. Yuzpe regimen (Estradiol plus levonorgestrel) has a pregnancy rate up to 2%.
Who can use emergencycontraception
Most women can use the emergency contraceptive methods. Pills such as levonogesterol and ellaone can be interfered if you are taking certain medication used to treat epilepsy, HIV or tuberculosis (TB), omeprazole, some less commonly used antibiotics (rifampicin and rifabutin). This is why you need to talk to pharmacist what medicines you are taking. They can advise you if they are safe to take with the emergency contraceptive pill.
IUD is not advised to be used by women or girls with untreated sexually transmitted infection (STI) or a pelvic infection; unexplained bleeding between periods or after sex. Most importantly about using Emergency IUD, it will not react with any other medicines you are taking. The IUD should not be inserted if there is a risk that you may already be pregnant.
Indication
Any women with the following conditions can use them:
• women who cannot use hormonalcontraception;
• Girls under 16 yearsold
• Totally unprotected intercourse,
• Coitus interrupts,
• Condom breakage or slippage,
• More than two missed oral contraceptive pills or pills started more than two days late,
• Sexual assault (not on oral contraceptive pill,
• Ejaculation into genitals,
• Delay in getting scheduled contraceptive injection,
• Expulsion of an intrauterine contraceptive device (IUD) or hormonal contraceptive implant,
• Failed withdrawal
How to take it ?
• Levonorgestrel can be taken as single dose regime 1.5 mg. It can be given in two doses as 0.75mg, 12 hours apart. Both forms are available over the counter without age restrictions
• Yuzpe regimen (Estradiol plus levonorgestrel) can be taken as 100 mcg of ethinyl estradiol plus 0.50 mg of levonorgestrel followed by the same pill regimen 12 hours later.
• Ulipristal is marketed as a single dose of 30 mg tablet under the brand name Ella or ellaOne. It is available but require prescription.
• Copper intrauterine contraception is generally inserted within five days after unprotected intercourse. It is done at health care facilities with skilled health proffeesionals.
If the woman vomits the pills, she might be offered placement of a copper IUD (if available) instead of oral emergency contraception. If levonorgestrel is vomited within three hours of administration, give antiemetic agent and then repeat the levonorgestrel.
Any regular contraceptive method can be started immediately after the use of levonorgestrel or estrogen-progestin emergency contraception.
Side effect
There are no serious or long-term side effects from taking the emergency contraceptive pill. However, it can cause Headaches, tummy pain, and changes to your next menstrual period. It can be earlier, later or more painful than usual, feeling or being sick. Antiemetics can be given to reduce nausea and vomiting. Menstrual bleeding after oral hormonal emergency contraception typically occurs within one week of the expected time. A pregnancy test should be performed if bleeding has not occurred within three weeks or if there is persistent vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain. There are some misconception about emergency contraception. Emergency contraception does not cause abortion, birth defects if has occured, EC are not dangerous to a woman’s health, do not promote risky sexual behavior, and do not make women infertile.
Recommendations
We strongly recommend emergency contraception to every women and girl who think that they can get pregnancy especially after unprotected sex, missing contraception or anyone meeting conditions above. Proper use of EC methods prevent getting pregnancy by over 99%. With EC, you prevent all risks related to pregnancy, abortion and its related complications. It offer additional chance to decide on child bearing. All ages are eligible to emergency contraception. All methods are available to almost all health care facilities from health center to referral hospitals, private clinics and all pharmacies.
Women should own all right to decide on their health regarding pregnancy. It should be responsibility to every healthcare provider to facilitate women or girl coming for EC and reduce judgement over young girls. Health decision makers, private sector and all related institutions should intervene to let teenagers and women have a choice over bearing pregnancy by making EC affordable even for teens of limited financials ability. They should also set strategic planning and equip community with accurate information. EC will save billions of USD spent on managing 25 million unsafe abortion that occur yearly, and unintended pregnancies.
Written by Philemon NISINGIZWE , a medical student at University of Rwanda.
Reference:
1. Andrew M Kaunitz, MD , uptodate ( feb 2019), Emergency contraception [ online ]. Availlable from: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/emergency- contraception
2. NHS, ( 2018, Feb) , Emergency contraception (morning after pill, IUD) [online]. Available from : https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/contraception/emergency-contraception/
3. WHO, (2018, feb) Emergency contraception [online]. Available from : https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/emergency-contraception
4. Dr Miriam Kaufman, ncbi, (2003 Mar), emergency contraception [online




3 Comments
Carine Urusaro
08 July 2019 02:28Honorine Cyuzuzo
08 July 2019 02:33Zebadia Martin
30 January 2020 21:41