Hyperbilirubinemia also called jaundice refers to an excessive level of accumulated bilirubin in the blood and is characterized by a yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclerae, mucous membranes and nails.it Occurs in 60% of term and 80% of preterm neonates.
However, significant jaundice occurs in 6 % of term babies, the Visible form of bilirubinemia: Newborn skin >5 mg / dl
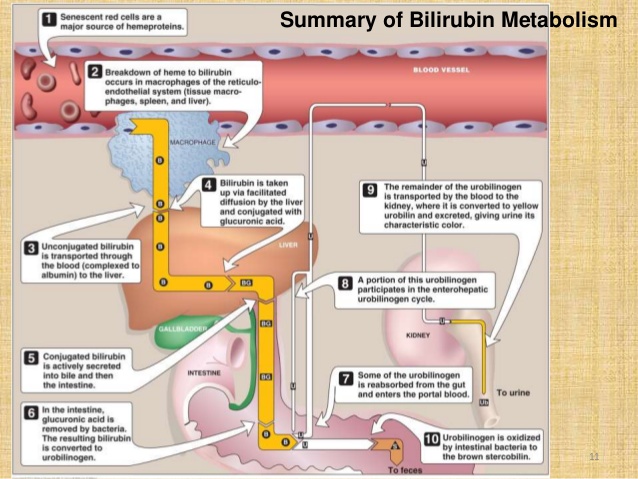
Mechanism of Bilirubin Metabolism
The red blood cells are highly produced by bone marrow and has life span of 120 days. With age, red blood cells become increasingly fragile and are damaged by passing through narrow capillaries. Macrophages in the liver and spleen phagocytize damaged red blood cells. As red blood cells are lysed, they release hemoglobin. Hemoglobin from the decomposed red blood cells is converted into heme and globin. Heme is decomposed into iron which is stored or recycled and biliverdin and bilirubin. Bilirubin (unconjugated or indirect) is bound to serum albumin and transferred to the liver where it is conjugated to glucoronate by glucuronyl transferase. Conjugated (direct) bilirubin is excreted into bile. A fraction of bilirubin from the stool is reabsorbed into the blood via the portal circulation (enterohepatic circulation).
For neonates, Bilirubin production is elevated because of increased break down of fetal erythrocyte. This is the result of shortened lifespan of fetal erythrocytes and high erythrocyte mass in neonates.
Hepatic excretory capacity is low because of low concentration of the binding protein ligandin in the hepatocytes and also because of low activity of glucuronyl transferase; the enzyme responsible for binding bilirubin to glucuronic acid, thus making bilirubin water soluble (conjugation).
TYPES OF JAUNDICE
There are two types of jaundice which are physiological and pathological jaundice.
Physiological jaundice
This jaundice appears after 24 hours its maximum intensity by 4th-5th day in term & 7th day in preterm with Serum level less than 15 mg / dl and it disappears without any treatment.
Causes of Physiology Jaundice
-
Increased bilirubin load
-
Defective uptake from plasma
-
Defective conjugation
-
Decreased excretion (ineffective hepatic excretion of unconjugated bilirubin)
-
Increased entero-hepatic circulation (unconjugated bilirubin is reabsorbed from intestine through the process of enterohepatic circulation)
-
Low bacterial degradation of bilirubin (in neonates, the bacterial degradation of bilirubin is reduced because the intestinal flora is not fully developed and this may lead to absorption of unconjugated bilirubin.
Pathological Jaundice
It appears within 24 hours of age, bilirubin increases by > 5 mg / dl / day, Serum bilirubin > 15 mg / dl, Direct bilirubin> 2 mg / dl and the total serum bilirubin level is above physiological level. Conjugated hyperbilirubinaemia is always pathological and may reflect metabolic liver disease, e.g. cystic fibrosis, organic acidosis, or congenital infection. The jaundice persisting after 14 days, Stool clay / white colored and urine staining clothes yellow. There are signs and symptoms of illness in the baby.
CAUSES OF PATHOLOGICAL JAUNDICE
-
Hemolytic disease: Rh, ABO incompatibility
-
Infections: malaria, bacterial
-
G6PD deficiency; Sepsis; Polycythemia
-
Intraventricular hemorrhage; Increased entero-hepatic circulation
-
Cephalohaematoma; Neonatal hepatitis
-
Extra-hepatic biliary atresia
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF JAUNDICE
- Skin color: unconjugated jaundice is lemon yellow; conjugated jaundice is nearer green
- Changes in muscle tone, seizures, or altered cry characteristics
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Petechiae
- Hemolytic anemia; Signs of Sepsis
- Stool color for pathological jaundice is clay or white colored and urine staining clothes yellow.
Investigation
Measurement of Bilirubin level (direct and total bilirubin)
- Blood type and Rh determination in mother and infant
- Direct antiglobulin test (DAT) in the infant (direct Coombs test)
- Hemoglobin and hematocrit values
– Ultrasonography
-AST; ALT
- Determining the caudal progression of jaundice. The jaundice starts around the head and the face and then progress to the shoulder, arms and the rest of the body.
-The skin level of jaundice can be used as a rough guide in the estimation of total bilirubin in newborns with jaundice in a resource limited settings where testing bilirubin level cannot be done.
MANAGEMENT OF JAUNDICE
-
Initiate early feeding: early breast feeding will help in reduction of breast feeding.
-
Drugs use of phenobarbital promote liver enzymes and protein synthesis.
-
Offer IV fluids between feeding: this is the best way to prevent dehydration and increases bilirubin excretion through urine.
-
ABO group and Rhesus incompatibility: give gamma globulin, iv, 500 mg/kg over 1 hour, repeat once after 6–8hours.
-
Reduction of bilirubin levels: phototherapy, exchange transfusion (breast milk and other types of non-physiologic jaundice such as
1. Breastfeeding jaundice: this the jaundice due to inadequate intake of breastmilk
2. Jaundice due to infection: this is the jaundice caused liver infection such as hepatitis and parasite (malaria).
3. Obstructive jaundice this types of jaundice is developed due to bile duct obstruction which prevent the flow of bile from bloodstream to intestine.
4. Endocrine jaundice: this the jaundice caused by endocrine disorder called hyperthyroidism (hyper metabolism due to hyperthyroidism increases the hepatic oxygen consumption without increasing the hepatic blood flow and this interfere with bile transport) and this is rare.
5. Hemolytic jaundice: is the jaundice caused by rhesus and ABO incompatibility and G6PD deficiency.
The image below shows when phototherapy and exchange transfusion is done according to age and bilirubin level
Complication
Kernicterus
Kernicterus Is a complication of untreated hyperbilirubinaemia (high level of bilirubin in the Blood). In newborn babies with hyperbilirubinaemia, the bilirubin can cross the membrane (thin layer of tissue) That separates the brain and the blood. The bilirubin causes yellow staining of the brain, and can damage the brain and spinal cord. This may result in short-term or long-term brain damage, or even death.
Brain damage caused by high levels of bilirubin is also called bilirubin encephalopathy.
Long-term symptoms of kernicterus include:
-
cerebral palsy – a condition that affects a child's movement and co-ordination
-
hearing loss – which can range from mild to severe
-
learning difficulties
-
involuntary twitching of different parts of their body
-
problems maintaining normal eye movements – people affected by kernicterus have a tendency to gaze upwards or from side to side rather than straight ahead
-
poor development of the teeth
Prognosis
Early recognition and treatment of hyperbilirubinemia prevents severe brain damage and it is curable.
References
DAIN, D. C., 2019. reseau naissance. [Online]
Available at: https://www.reseau-naissance.fr/medias/2019/04/20190402-C.-DAIN-Ictere-et-allaitement-maternel.pdf
[Accessed 24 september 2019].
Stuart Crisp, J. R., 2013. Emergencies in pediatrics and neonatology. 2nd ed. Great Clarendon Street, Oxford OX2 6DP: Oxiford University Press.
Neonatology at a Glance, 2nd edition. Edited by Tom Lissauer & Avroy A. Fanaroff. © 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd page (39-45)
https://pt.slideshare.net/madcatz21/bilirubin-metabolism-67992625/11
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4935699/
Written by BERWA Aurore student nurse in University of Rwanda Year 3.



3 Comments
Dr. Emmanuel
07 June 2020 13:55Berwa
07 June 2020 15:27Cyuzuzo Em�rance
07 June 2020 15:32