Acne is a common disease affects hair follicles and sebaceous glands (pilosebaceous units) with many forms and varying severity. It negatively affects the quality of life and hence the understanding of acne is of essence for adolescents and parents.
What is the prevalence of Acne?
It is prevalent in adolescents in whom the gonads start to produce high amounts of androgen hormones. It is estimated that 85% of people of 12 to 24 years develop mild acne in the lifetime. Other age groups may be affected and this article discusses acne in adolescent population only.
What are the signs and symptoms of acne vulgaris?
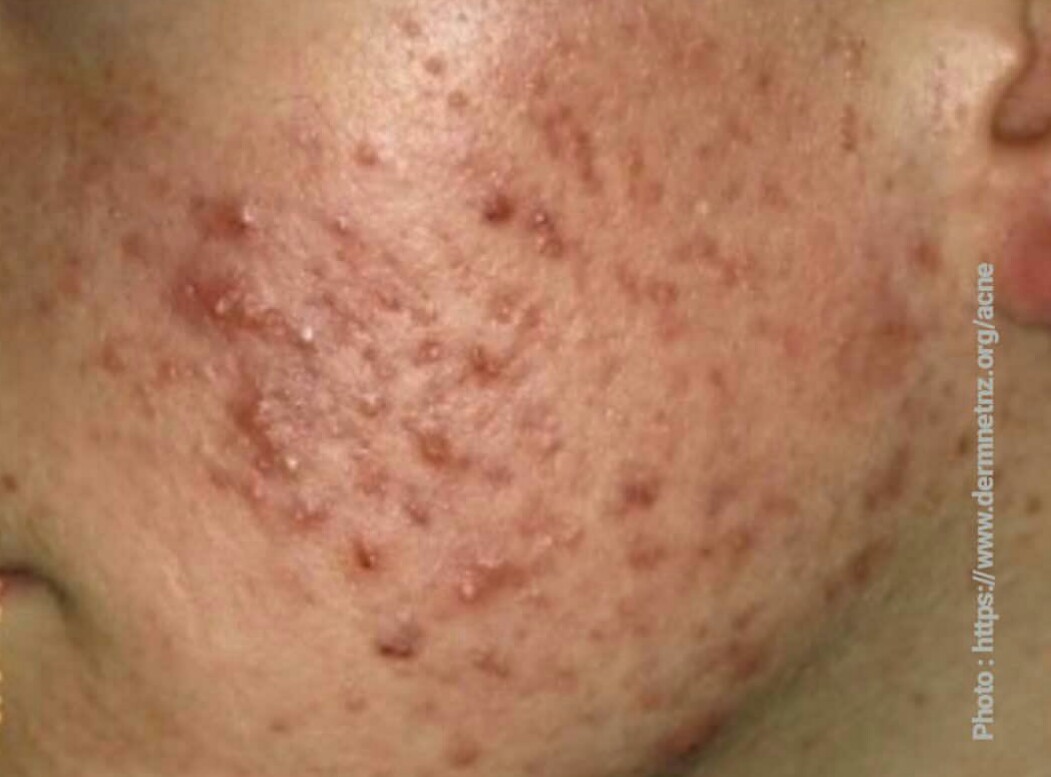
Classically, acne will manifest as pimples of varying sizes and color in the high rich parts of body in the sebum producing glands like face, chest and upper back. There may be also pain, tenderness or reddnes. Systemic symptoms are rare unless you develop the most severe forms of acne and/or acne is associated with Polycystic Ovarian syndrome (PCOS) seen in female patients where patients develop oligomenorrhea (infrequent menstrual periods than usual), hirsutism (conditionof unwanted, malepattern hair growth in women), insulin resistance (Acanthosis neglicans) in addition to the acne itself.
What are the causes of acne vulgaris?
Genetic predisposition (susceptibility) is the important underlying cause of acne. Other causes include cosmetic agents, certain medications (steroids, lithium, pomades among others), conditions associated with increased androgen production like PCOS (see above).
In addition, diet is one of important factors affecting acne especially high carbohydrate diet that affect certain pathways in acne development.
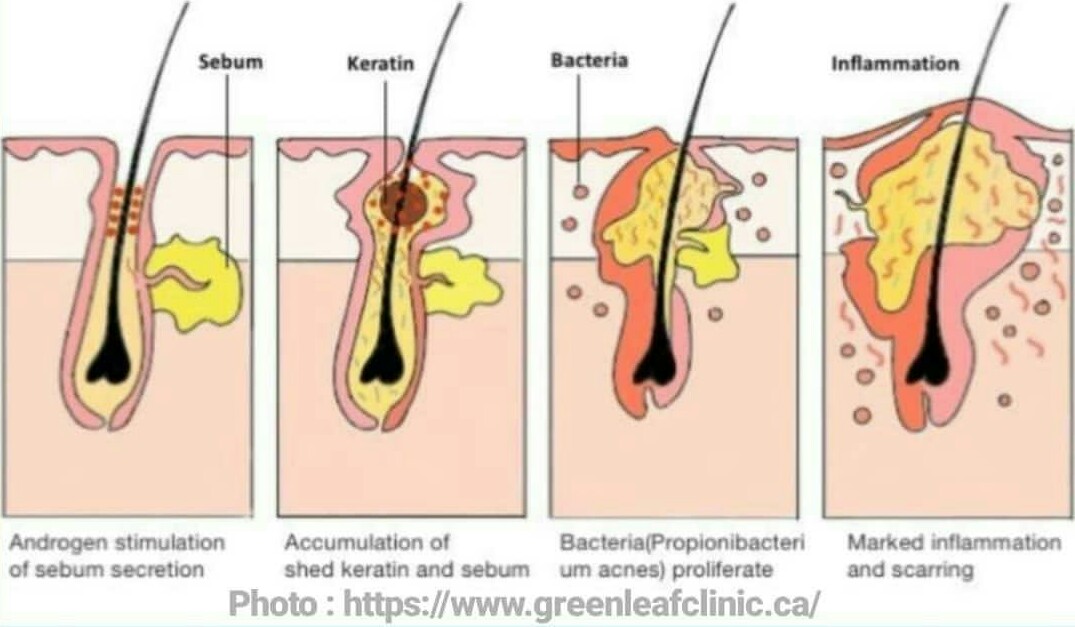
Acne is a disease of hair follicles and its lesions are follicular centered. Four mechanisms are involved in its onset including (1) hormonal changes,(2) excessive sebum production,(3) fluctuation in micro-organisms mainly bacteria called cutibacterium acnes (formerly known as propionibacterium acnes) residing in these so called hair follicles, and finally (4) accumulation of dead cells in hair follicle.
All these factors lead to the obstruction of hair follicle and /or inflammation in pilosebaceous unit (hair follicles and associated sebaceous glands). These are are the targets of medical management of acne.
What are the complications of untreated acne vulgaris?
Acne is associated with long-lasting and detrimental psychological effects like depression, anxiety, low self-esteem and suicidal ideation and physical effects like scarring and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation which are dark spots in previous acne lesions.
Hence, for the better outcomes, affected adolescents should seek medical help (dermatologists or other qualified medical practitioners) for early assessment of their diseases status and management.
How is acne vulgaris treated?
Treatment includes topical drugs/creams (antibiotics, retinoids,…) applied on the skin and/or systemic drugs (usually given orally).Treatment could take up to months and hence good compliance is essential for better results. In the next article, I will discuss the healthy lifestyles to prevent and improve acne vulgaris.
About author:
Dr. NDAGIJIMANA Jean Bosco
Trainee in Dermatology, Venereology and Andrology at Alexandria University, Egypt
Editor: Esther G. Njuguna
Bibliography
Oakley, A. (2014, June). Acne vulgaris. Retrieved 2019, from https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/acne-vulgaris/
Oakley, A. (2014). DermNet NZ. Retrieved August 26, 2019, from https://www.dermnetnz.org/: https://www.dermnetnz.org/topics/acne-vulgaris/
Rao, J. (2019, March). Acne Vulgaris. Retrieved August 2019, from https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1069804-pathophysiology
Various cuses of acne. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.greenleafclinic.ca/acne-vancouver/
Zulu T.P, Mosam A., Balakrishna Y.& Dlova N.C. (2017). Acne in South African black adults: A retrospective. SAMJ, 1106-1109.



2 Comments
Emmanuel Ndayisaba
01 October 2019 18:36Zebadia Martin
01 October 2019 19:13